In today’s comprehensive guide, we delve into the multifaceted world of diabetes—from understanding its stages, symptoms, and diagnosis to exploring the daily experiences of living with the condition.
This guide illuminates essential strategies for managing diabetes through balanced nutrition, personalized treatment protocols, and thoughtful lifestyle adjustments such as hydration, healthy bedtime snacks, and consistent daily routines.
Additionally, it discusses proactive approaches to potentially reversing and managing the disease over the long term, while also highlighting the critical financial and social support systems that empower patients to thrive.

Success is knocking! Open the door at Great Life Worldwide and learn why it’s your key to prosperity. Free tour available – act fast!
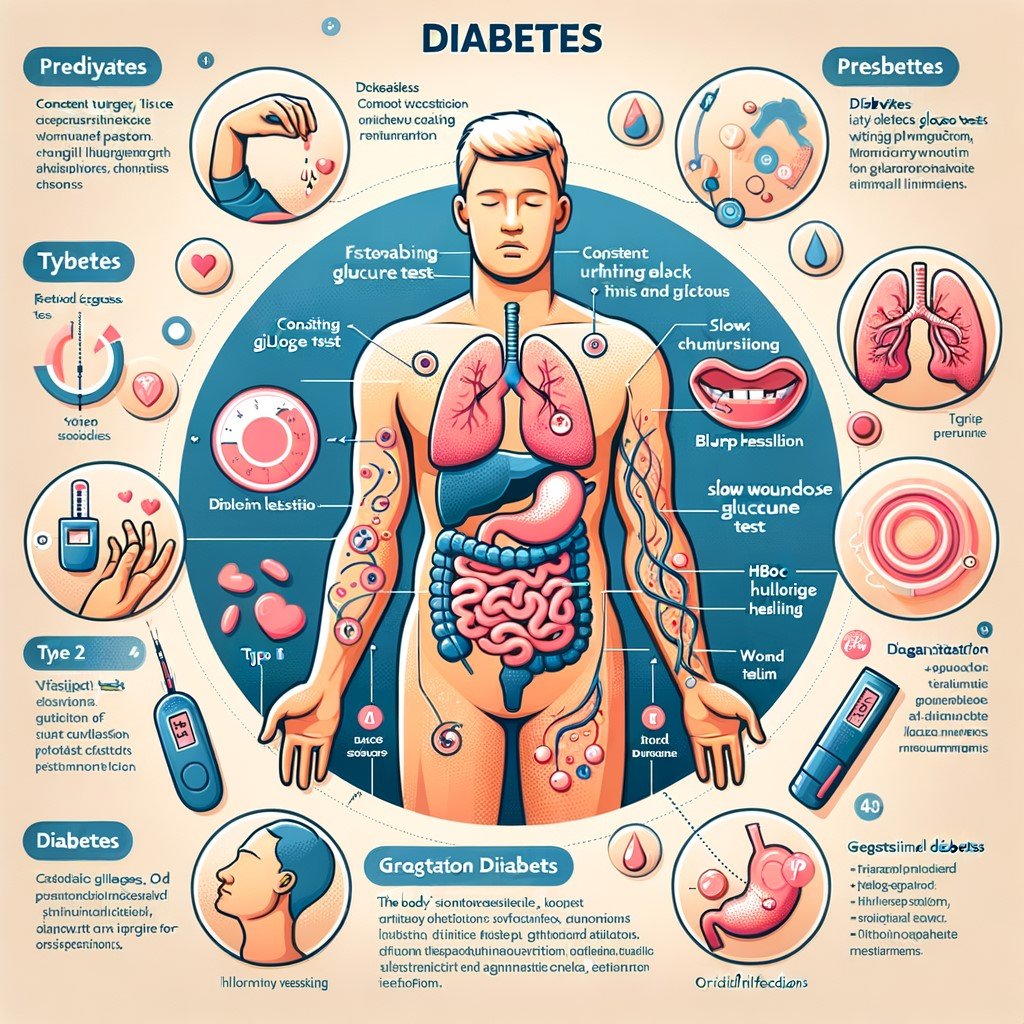
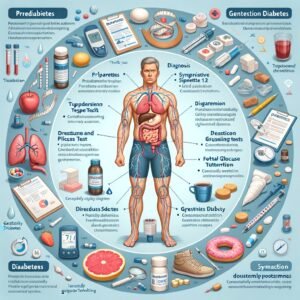
1. Understanding Diabetes: Stages, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic condition marked by the body’s inability to effectively regulate blood glucose levels. This impairment emerges from either insufficient insulin production or the body’s resistance to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar that can result in severe health complications if unmanaged.
Clinicians typically categorize diabetes into several stages, including prediabetes, where blood sugar levels are elevated yet not high enough for a definitive diabetes diagnosis, followed by clinically diagnosed diabetes, which encompasses both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
In Type 1 diabetes, an autoimmune response leads to the destruction of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, while Type 2 diabetes generally develops due to lifestyle factors and genetic predisposition, culminating in insulin resistance. Gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy, also represents a distinct classification that requires vigilant monitoring to protect both maternal and fetal health.
Understanding the symptoms is critical for early detection and effective management. Common indicators of diabetes include persistent hunger and fatigue, along with frequent urination and unusual weight fluctuations. Blurred vision, slow wound healing, and recurrent infections are also signs that warrant further investigation.
To accurately diagnose this condition, healthcare providers employ a combination of blood tests, including fasting plasma glucose tests, the HbA1c measurement, and oral glucose tolerance tests. These diagnostic tools allow for a thorough evaluation of an individual’s glycemic control over time and assist in determining the appropriate stage and severity of the disease.
A comprehensive understanding of the stages, symptoms, and diagnostic procedures of diabetes empowers patients and clinicians alike. It fosters early intervention, personalized treatment plans, and proactive management of potential complications while ensuring informed decision-making in clinical practice. In-depth analysis and continuous monitoring are essential components that enhance the ability to manage the condition. Regular consultations with specialists play a pivotal role in customizing management strategies.
Your dream life is calling! Answer at Great Life Worldwide and see how it can make it a reality. Claim your free tour now!
2. Experiencing Diabetes: How It Feels and Body Responses
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that triggers distinct sensations and physiological changes in individuals, eliciting a range of experiences that vary from person to person. Many patients first encounter subtle signs such as persistent fatigue, blurred vision, or unusual thirst, which may gradually progress into more noticeable shifts. The body’s response to fluctuating blood glucose levels triggers these sensations, often leaving individuals feeling both physically and emotionally taxed.
From a physiological standpoint, the regulation of insulin and glucose metabolism is pivotal. An imbalance in insulin secretion can lead to either hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia, each accompanied by a unique set of symptoms.
Hyperglycemia typically manifests as increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss. Conversely, hypoglycemia might result in shakiness, dizziness, confusion, and even a sense of heightened anxiety.
Furthermore, the daily experience of diabetes is not solely linked to these acute changes; patients often describe an underlying fatigue and a sense of vulnerability regarding their long-term health. Such physical reactions can be compounded by emotional stress, leading to challenges in managing daily activities and a heightened awareness of the body’s signals. Professional medical management and regular monitoring play essential roles in mitigating these responses and helping patients better understand their individual symptoms.
Emphasizing the importance of personalization, healthcare providers often recommend tailored treatment regimens that address both physical and emotional well-being. By paying close attention to body responses and actively managing symptoms, patients are better equipped to navigate the practical challenges of living with diabetes while striving for optimal health outcomes.
This ongoing interplay between clinical management and daily life underscores the necessity for continuous education and adaptation in treatment strategies. Patients benefit from a composed and informed approach that empowers them to respond effectively to both predictable and unforeseen bodily changes. Continual collaboration with healthcare professionals remains invaluable.

Tired of the ordinary? Embrace the extraordinary at Great Life Worldwide! Discover the amazing opportunities and take a free tour today.
3. Safe Nutrition and Meal Choices: Foods to Eat and Avoid
Establishing a balanced meal plan is essential in managing diabetes effectively. Nutrition plays a significant role in moderating blood glucose levels, and careful selection of foods can help minimize rapid sugar spikes while supporting overall health.
A focus on high-fiber foods and lean protein is recommended to maintain steady energy levels. Emphasizing whole grains, vegetables, and fruits contributes essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are crucial for individuals seeking to manage their diabetes safely.
Intake of complex carbohydrates, such as quinoa, barley, and whole wheat, is preferable over refined carbohydrates. Consumers should prioritize nutrient-dense options by ensuring that meals contain a variety of vegetables and lean proteins, including fish, poultry, and plant-based alternatives like legumes.
Healthy fats from sources such as olive oil, avocados, and nuts further assist in optimizing glycemic response. Portion control should be integral to any meal plan, as carefully measured servings can prevent overconsumption and potential glycemic imbalances.
Conversely, limiting foods that contribute to rapid blood sugar surges is also vital. Processed foods, sugary beverages, and snacks that are high in added sugars may exacerbate glycemic instability. Additionally, saturated fats typically found in red meat and full-fat dairy products should be consumed sparingly, while trans fats should be avoided entirely. Individuals are encouraged to read nutrition labels meticulously to better understand the impact of each food item on their overall diabetes management plan.
Adopting these nutritional strategies enables a structured approach to meal planning while reducing the potential complications of diabetes. This professional framework supports informed dietary choices and promotes effective diabetes control, combining scientific evidence with practical recommendations for a balanced lifestyle.
Collaborating with healthcare professionals, including dietitians, ensures personalized guidance. Regular monitoring of blood sugar responses further refines meal choices, thereby enhancing long-term diabetes management and overall well-being for significantly improved health outcomes daily.
4. Managing Treatment: Insulin Use, Fasting, and Medication Protocols
Effective management of diabetes relies on tailoring treatment strategies uniquely to each patient. Among these strategies, insulin administration stands as a cornerstone for many, ensuring that blood glucose levels are efficiently regulated. Insulin usage requires precision in dosage and timing, as even minor inconsistencies can lead to severe fluctuations. Medical professionals emphasize the importance of contextualizing treatment regimens according to individual lifestyle factors, dietary habits, and overall health status.
In tandem with insulin, fasting protocols have gained attention in recent studies as potential adjunct therapies. Carefully monitored fasting, when integrated under professional guidance, can enhance insulin sensitivity and promote metabolic balance.
However, adopting fasting routines necessitates a clear understanding of personal health limitations and potential side effects. Treatment plans should incorporate flexible fasting schedules that align with medication timing, minimizing risks associated with hypoglycemia and other related complications.
Additionally, an assortment of oral medications and adjunct injections contribute to comprehensive diabetes management. These therapies, including metformin, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and other novel agents, function by optimizing blood sugar control and improving the body’s natural responses to insulin.
Adherence to prescribed medication protocols is vital; patients must engage in regular follow-ups to gauge treatment efficacy and adjust regimes accordingly. Professionals recommend that clinicians continually refine treatment strategies based on emerging research and patient feedback to ensure optimal outcomes.
Within this framework, collaboration between healthcare providers and patients is essential. Clear communication regarding treatment expectations, potential side effects, and dosage adjustments fosters a safe and adaptive management environment. Emphasizing personalized assessment, this integrated approach to insulin use, fasting, and medication protocols encourages both short-term stability and long-term health improvement.
Regular monitoring of glucose trends and open dialogue with a multidisciplinary team further empower individuals to make timely adjustments, ensuring that treatment regimens remain synergistic with evolving health needs and lifestyle choices effectively.
Seeking adventure? Embark on a journey to success at Great Life Worldwide! Learn about it and take a free tour. Don’t miss the boat!
5. Lifestyle Adjustments: Hydration, Bedtime Snacks, and Daily Routines
Effective diabetes management extends beyond medication and blood sugar monitoring to include thoughtful lifestyle adjustments that support overall health. Prioritizing hydration is fundamental, as maintaining adequate fluid intake assists in the optimal functioning of various metabolic processes.
Water consumption helps the body regulate temperature, transport nutrients, and flush out toxins, thereby supporting steady blood glucose levels. It is beneficial for individuals with diabetes to establish regular water-drinking habits and consult health professionals to tailor fluid recommendations to their specific needs.
In parallel, incorporating a strategically planned bedtime snack can be crucial for sustaining balanced glucose levels overnight. Light snacks that combine lean protein, healthy fats, and low-glycemic carbohydrates help prevent nocturnal hypoglycemia while avoiding a rapid surge in blood sugar levels before sleep. Options such as a small serving of unsalted nuts paired with a slice of cheese or a modest portion of Greek yogurt with a few berries can provide the right balance without overwhelming the system.
Establishing consistent daily routines further reinforces these efforts. A structured schedule that includes set meal times, regular physical activity, and consistent sleep patterns contributes significantly to metabolic stability. Routine exercise, even in moderate forms like brisk walking or cycling, enhances insulin sensitivity and supports weight regulation, which is beneficial for long-term diabetes management.
Additionally, aligning sleep schedules and incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness or gentle stretching can have a notable impact on blood sugar control. By embracing these lifestyle adjustments—focusing on consistent hydration, thoughtful bedtime nutrition, and balanced daily routines—individuals are better equipped to maintain optimal health and manage diabetes effectively on a day-to-day basis.

Craving a taste of success? Savor it at Great Life Worldwide! Discover the delicious opportunities and take a free tour now.
6. Reversing and Managing Diabetes: Strategies for Long-Term Health
Reversing and managing diabetes is an ambitious objective that requires a sustained commitment to education, lifestyle modifications, and professional guidance. A comprehensive strategy integrates nutritional adjustments, physical activity, behavioral changes, and medication optimization. Personalized care plans developed in collaboration with healthcare providers consider individual metabolic profiles, family history, and long-term health goals to tailor effective interventions.
Prioritizing nutrient-dense foods, minimizing refined carbohydrates, and including whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats are essential components of nutritional planning that aid in stabilizing blood glucose levels. Regular physical exercise, including moderate aerobic activities and resistance training, enhances insulin sensitivity, supports weight management, and contributes to improved cardiovascular health.
Behavioral interventions also play a critical role in diabetes management. Setting realistic, incremental goals promotes steady progress and fosters confidence in making lifestyle changes. Structured support from diabetes educators and counselors assists in developing coping strategies for stress and potential setbacks.
Incorporating mindfulness practices, such as meditation and yoga, helps reduce stress-induced blood sugar fluctuations while reinforcing long-term healthy habits. Technological tools, including continuous glucose monitors and mobile health applications, further empower patients by providing real-time insights that inform personalized adjustments.
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals ensure that evolving needs are met through timely medication adjustments and lifestyle refinements. Although complete reversal of diabetes may not be attainable for every individual, consistent management strategies significantly improve glycemic control and reduce the risk of complications. Through a multifaceted, patient-centered approach that balances clinical guidance with personal commitment, individuals can achieve sustainable improvements in their overall health and vitality.
Effective diabetes management requires continuous self-monitoring and adjustment of daily routines, as well as ongoing education to adapt to new advancements in medical research. Integrating community support and accessing emerging technological innovations further optimizes long-term outcomes. These proactive measures lead to improved overall quality of life.
7. Financial and Social Benefits: Support, Claims, and Diabetic Resources
Understanding the broader impacts of diabetes management extends beyond clinical care to encompass significant financial and social benefits. Individuals dealing with diabetes have access to a variety of resources designed to ease the economic burden associated with ongoing medical expenses, nutritional guidance, and technological aids.
Many healthcare systems offer targeted programs enabling patients to claim subsidized costs related to medication, insulin delivery systems, and routine check-ups. This financial support not only relieves families financially but also encourages timely medical interventions, reducing the likelihood of severe complications.
Additionally, specialized support networks and community-based organizations provide vital social assistance, connecting patients with peers, healthcare professionals, and advocacy groups. These connections foster environments where experiences and successful management strategies are shared, enhancing the overall quality of life.
Patients enrolled in diabetes support groups benefit from well-organized information sessions, counseling services, and even employment aid, which collectively contribute to improved mental health and reduced feelings of isolation.
The availability of governmental and non-governmental programs plays a crucial role in facilitating health insurance claims and securing necessary financial aid. Awareness of these programs empowers patients to pursue appropriate claims and maintain a robust, transparent relationship with their healthcare providers.
Furthermore, disease-specific resource centers offer a wealth of educational materials and customized support programs, ensuring that individuals stay informed about the latest treatment advancements and research initiatives.
In essence, the combination of financial assistance and community support provides a comprehensive safety net, enabling diabetic individuals to manage their condition with confidence while mitigating the associated socio-economic challenges.
This integrative approach is pivotal for fostering long-term wellness, as it aligns medical treatment with accessible, supportive services aimed at enhancing overall quality of life. Access to these financial and social benefits empowers diabetic individuals to achieve sustained well-being.
Your success is waiting! Claim it at Great Life Worldwide and see how it can propel you forward. Take the free tour before time runs out!
Conclusion:
This guide serves as a vital resource for anyone navigating the complexities of diabetes, offering clear insights and actionable strategies for managing the condition. By integrating medical knowledge with practical lifestyle tips and support mechanisms, the content underscores the importance of personalized care and continuous education. Ultimately, embracing a comprehensive approach fosters improved health outcomes and enhances quality of life, empowering individuals to confidently manage diabetes and thrive in their everyday lives.