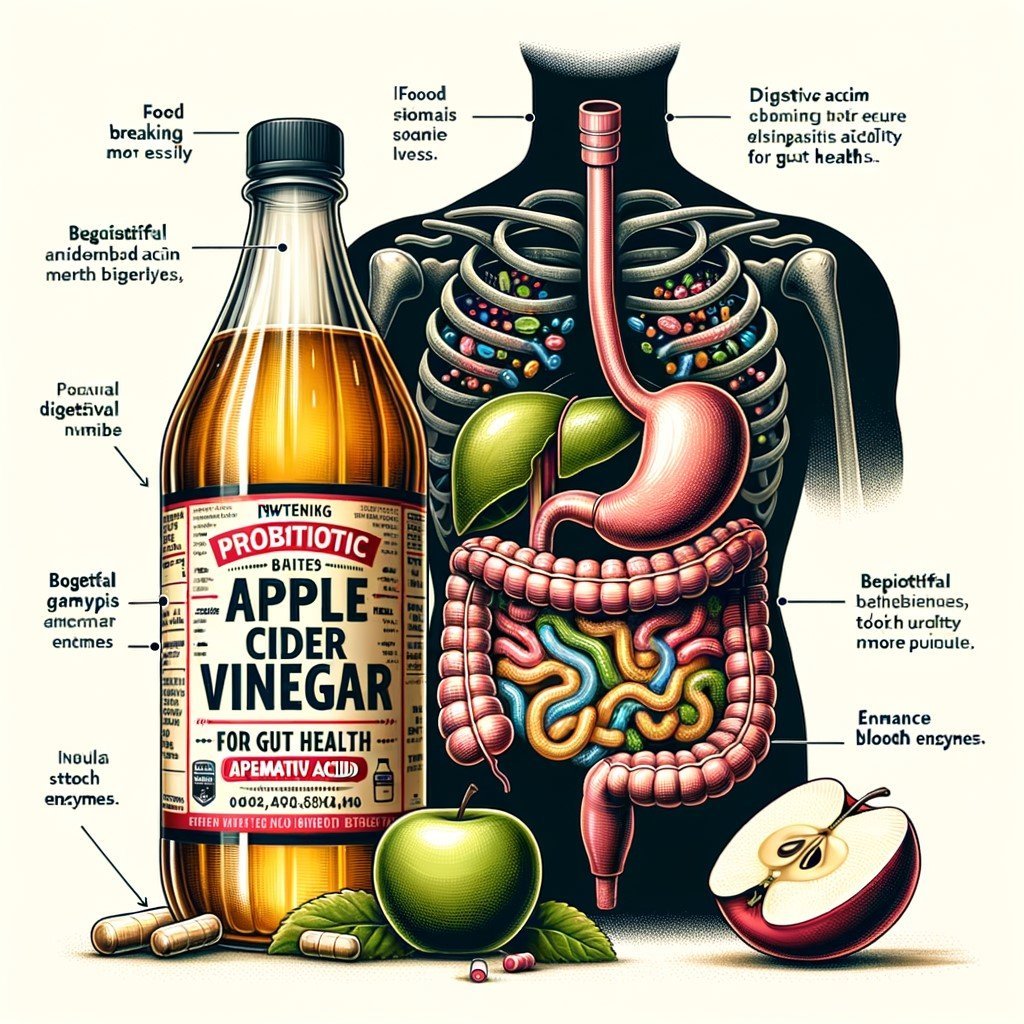
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) has become a popular topic in the realm of health and wellness, particularly for its purported benefits on gut health. This comprehensive guide delves into various aspects of ACV’s impact on digestion, including its potential advantages when combined with probiotics and digestive enzymes, as well as considerations regarding dosage and safety. By exploring both the scientifically-backed benefits and common misconceptions surrounding ACV, this article aims to provide a balanced perspective for those interested in incorporating it into their dietary regimen.

Success is knocking! Open the door at Great Life Worldwide and learn why it’s your key to prosperity. Free tour available – act fast!
1. Understanding the Benefits of Apple Cider Vinegar for Digestion
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) has garnered attention for its potential digestive benefits, attributed primarily to its acetic acid content. Acetic acid is known to enhance the body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients from food, thereby promoting overall digestive health. By increasing stomach acidity, ACV can aid in breaking down proteins more efficiently and facilitate smoother digestion.
Moreover, apple cider vinegar may help regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the rate at which food leaves the stomach and enters the lower digestive tract. This process can prevent spikes in blood glucose levels after meals, contributing to a more balanced metabolic response.
Another notable benefit of ACV is its prebiotic properties. Prebiotics are compounds that nourish beneficial gut bacteria, supporting a healthy balance of the microbiome, which is crucial for optimal digestion and immune function. The fermentation process used to produce apple cider vinegar results in the presence of pectin, a type of soluble fiber with prebiotic properties, which further enhances gut health.
Additionally, some studies suggest that ACV might alleviate symptoms associated with indigestion or heartburn by neutralizing stomach acids due to its alkaline-forming nature once metabolized by the body. However, it’s important to note that these claims require further scientific validation through comprehensive research.
While incorporating apple cider vinegar into your diet could offer various digestive advantages, it should be consumed responsibly and as part of a balanced diet tailored to individual needs. Consulting healthcare professionals before making significant dietary changes ensures the safe and effective use of tailored nutrition plans, specifically addressing personal health conditions or concerns related to digestion.
Nourish Your Body, Fuel Your Potential—Start with GreatLife Supplements.
2. Combining Apple Cider Vinegar with Probiotics and Digestive Enzymes
The synergistic combination of apple cider vinegar (ACV) with probiotics and digestive enzymes presents a promising approach to enhancing gut health. ACV, known for its acetic acid content, can create an acidic environment in the stomach that aids in breaking down food more efficiently. This process not only facilitates digestion but also supports the growth of beneficial bacteria by maintaining an optimal pH level.
Probiotics, which are live microorganisms that confer health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts, work harmoniously with ACV to promote a balanced gut microbiome. The acidic nature of ACV may enhance the survival rate of these probiotics as they transit through the harsh gastric environment to reach the intestines, where they exert their positive effects. By fostering a diverse microbial ecosystem, this combination can help improve nutrient absorption and reduce gastrointestinal discomfort.
Digestive enzymes further complement this trio by catalyzing the biochemical reactions necessary for breaking down macronutrients, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and fats, into absorbable units. When combined with ACV’s acidity and probiotic support, digestive enzymes can help optimize nutrient breakdown and assimilation, potentially alleviating symptoms such as bloating or indigestion.
However, it’s crucial to consider individual tolerance levels when integrating these components into one’s diet. While many people may experience enhanced digestive function from this combination, others might find it too potent or irritating if consumed excessively or on an empty stomach. Consulting healthcare professionals before starting any new supplement regimen is advisable to tailor approaches based on personal health needs.
In conclusion, while combining apple cider vinegar with probiotics and digestive enzymes holds potential benefits for gut health enhancement through improved digestion and microbial balance, personalized consideration remains key to maximizing efficacy without adverse effects.
Say Goodbye to Fatigue—Feel the GreatLife Energy Difference.
3. Potential Risks: Who Should Avoid Apple Cider Vinegar?
While apple cider vinegar (ACV) is celebrated for its potential health benefits, it’s crucial to recognize that it may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain medical conditions or those taking specific medications should exercise caution when considering ACV as a dietary supplement.
Firstly, individuals with gastrointestinal issues such as ulcers or acid reflux should avoid consuming ACV. The high acidity of vinegar can exacerbate these conditions, leading to increased discomfort and irritation of the stomach lining. Similarly, those suffering from gastroparesis—a condition where the stomach cannot empty properly—should steer clear of ACV, as it may further delay gastric emptying.
People with diabetes need to be particularly cautious when incorporating ACV into their regimen. While some studies suggest that ACV can help regulate blood sugar levels, it can also interact unpredictably with insulin and other diabetes medications. Diabetic patients should consult their healthcare provider before using ACV regularly.
Moreover, individuals on potassium-lowering medications or diuretics should avoid excessive consumption of apple cider vinegar due to its potential impact on potassium levels in the body. Low potassium levels can lead to muscle weakness and irregular heartbeats.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women are advised against using large amounts of apple cider vinegar without consulting a healthcare professional. The effects of concentrated acetic acid during pregnancy are not well-studied, and safety can’t be guaranteed.
Lastly, anyone with allergies or sensitivities to apples or fermented products should refrain from using apple cider vinegar until they have consulted an allergist or physician.
In summary, while apple cider vinegar offers numerous health benefits for many people, certain groups must approach its use cautiously due to potential risks associated with pre-existing health conditions and medication interactions.
4. Interactions with Medications: What to Know Before You Start
When considering the integration of apple cider vinegar (ACV) into your health regimen, it is crucial to understand its potential interactions with medications. While ACV is often lauded for its natural health benefits, it can interact adversely with specific prescriptions and over-the-counter drugs.
Firstly, individuals taking diabetes medications should exercise caution. ACV has been shown to lower blood sugar levels, which could amplify the effects of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents, leading to dangerously low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia). Monitoring blood glucose levels closely and consulting a healthcare provider before incorporating ACV is advisable for individuals taking such medications.
Secondly, people on diuretics or “water pills” may experience an imbalance in potassium levels when consuming ACV regularly. The acetic acid in vinegar can exacerbate potassium depletion caused by these medications, potentially resulting in hypokalemia—a condition characterized by muscle weakness and irregular heartbeats.
Moreover, those taking digoxin (Lanoxin), a medication used for heart conditions like atrial fibrillation or heart failure, should be aware that low potassium levels can increase the risk of digoxin toxicity. Given that ACV may contribute to reduced potassium levels when combined with certain diuretics or other factors that affect electrolyte balance, it’s essential to monitor and consult with a healthcare professional carefully.
Additionally, individuals using laxatives should note that combining them with ACV might lead to excessive gastrointestinal distress due to increased bowel movements or diarrhea.
In summary, while apple cider vinegar offers various health benefits related to gut health and beyond, understanding its interactions with specific medications is vital. Consulting healthcare professionals ensures safe usage tailored to individual medical needs and prevents adverse reactions that could compromise overall well-being.

Unlock Peak Performance—Personalized Nutrition Starts Here.
5. Debunking Myths: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Cleanse Your Intestines?
The notion that apple cider vinegar (ACV) can cleanse the intestines has gained traction in popular health circles, but it’s crucial to separate fact from fiction. While ACV does possess specific properties that may support digestive health, the idea of it acting as a cleansing agent for the intestines is vastly overstated.
Firstly, it’s essential to understand what “cleansing” implies. The human body already has efficient systems in place—namely, the liver and kidneys—that naturally detoxify and eliminate waste products. There is no scientific evidence supporting the claim that ACV enhances these processes or acts as an intestinal cleanser.
Apple cider vinegar contains acetic acid, which has been shown to have antimicrobial properties. This might suggest some potential in balancing gut bacteria; however, this effect should not be confused with cleansing or detoxifying actions. The presence of beneficial bacteria in unfiltered ACV could contribute positively to gut flora balance, but doesn’t equate to a thorough cleanse of the intestines.
Moreover, excessive consumption of apple cider vinegar can lead to adverse effects such as tooth enamel erosion and gastrointestinal discomfort due to its high acidity levels. These risks underscore the importance of moderation when incorporating ACV into your diet.
In conclusion, while apple cider vinegar may offer some benefits related to digestion through its probiotic content and mild antimicrobial effects, it should not be relied upon as a method for intestinal cleansing. Those interested in improving their digestive health are better served by focusing on a balanced diet rich in fiber, adequate hydration, and regular physical activity, rather than seeking quick-fix solutions like the supposed cleanses offered by products such as apple cider vinegar.

Your Health Journey Deserves the Best—Choose GreatLife Quality.
6. Effective Dosage: How Much is Beneficial for Digestion?
Determining the appropriate dosage of apple cider vinegar (ACV) for digestive health is crucial to harnessing its potential benefits while minimizing any adverse effects. While there is no universally agreed-upon dosage, most experts recommend starting with a conservative amount and adjusting based on individual tolerance and response.
A standard guideline suggests consuming one to two tablespoons (15-30 ml) of ACV diluted in a large glass of water before meals. This dilution not only helps mitigate the acidity but also aids in preventing potential damage to tooth enamel and esophageal lining. For those new to ACV, starting with one teaspoon (5 mL) per day is a prudent approach, gradually increasing as your body adapts.
It’s essential to note that excessive consumption of ACV may lead to undesirable side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort or erosion of dental enamel, due to its acidic nature. Therefore, moderation remains key when incorporating it into your daily routine.
For individuals seeking targeted digestive support, integrating ACV into meals rather than consuming it solely as a beverage might offer additional benefits. Using it as a salad dressing ingredient or adding it to marinades can enhance flavor while contributing positively to digestion without overwhelming the palate.
Moreover, consistency plays an essential role in achieving desired outcomes; sporadic use may not yield significant results. Establishing a regular intake pattern—whether daily or several times weekly—can help maintain digestive balance over time.
Ultimately, consulting with healthcare professionals before introducing apple cider vinegar into your regimen is advisable, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions or are taking medications that could interact adversely with its components. By adhering to recommended dosages and considering personal health factors, you can effectively incorporate apple cider vinegar into your dietary practices for optimal digestive well-being.
7. Exploring Weight Loss Claims: Does It Reduce Belly Fat?
The notion that apple cider vinegar (ACV) can aid in weight loss, particularly in reducing belly fat, has gained significant attention. However, it is crucial to examine these claims through a scientific lens to determine their validity.
Several studies suggest that ACV may contribute to modest weight loss when combined with a calorie-controlled diet and regular exercise. The primary mechanism attributed to this effect is acetic acid, the main component of ACV. Acetic acid is believed to enhance metabolism by increasing the enzyme AMPK, which boosts fat burning and decreases fat storage in the liver.
Moreover, some research indicates that consuming ACV before meals might promote satiety or feelings of fullness. This could potentially lead individuals to consume fewer calories throughout the day, indirectly supporting weight management efforts. A 2009 study found that participants who consumed vinegar daily experienced greater weight loss compared to those who did not.
Despite these findings, it’s essential to approach them with caution due to several limitations. Most studies have been small-scale and short-term; therefore, more extensive research is needed to provide conclusive evidence on long-term effects and safety. Additionally, while ACV may assist as part of a broader lifestyle change aimed at weight reduction, it shouldn’t be viewed as a standalone solution or miracle cure for obesity or excessive belly fat.
Furthermore, excessive consumption of ACV can lead to adverse effects such as digestive discomfort or erosion of tooth enamel due to its acidic nature. Therefore, moderation is key when incorporating it into your routine.
In conclusion, while there are indications that apple cider vinegar might support weight loss efforts by enhancing metabolic processes and promoting satiety, relying solely on it without making other dietary and lifestyle changes would likely yield limited results.

Ready to write your success story? Grab your pen at Great Life Worldwide! Learn about it and take a free tour. Don’t let this chance slip away!
Conclusion:
While apple cider vinegar offers several promising benefits related to digestion and overall gut health, it’s essential to approach its use with informed caution. Understanding who should avoid ACV due to potential risks or medication interactions is crucial for safe consumption. Moreover, while some claims about weight loss and intestinal cleansing are overstated, moderate use of ACV can complement a healthy lifestyle aimed at improving digestive function. Ultimately, consulting healthcare professionals before making significant changes ensures that any incorporation of apple cider vinegar aligns with individual health needs and goals.